What Is Azure Red Hat OpenShift?
Red Hat OpenShift provides a Kubernetes platform for enterprises. Azure Red Hat OpenShift permits you to deploy fully-managed OpenShift clusters in the Azure cloud. Azure Red Hat OpenShift is a joint collaboration between Microsoft and Red Hat—it is engineered, supported and operated by both companies, for the purpose of providing a centralized platform that fulfills all requirements.
Azure Red Hat OpenShift has the following tools and functionality in one platform to help both operations and development teams:
- Image registries
- Storage management
- Networking solutions
- Logging and monitoring tools
The Importance of Azure Red Hat OpenShift
OpenShift offers the resources, tasks and tools needed to run containers in the production environment via Kubernetes, and which has to be tested and versioned together. When developing containerized applications, you require integration with databases, frameworks, CI/CD tools and middleware.
This service lets you sign-on through Azure Active Directory (AD). The clusters are located in your Azure subscriptions and are featured in your Azure bill.
When using Azure Red Hat OpenShift, you are not required to perform patches or operate VMs. Microsoft and Red Hat are responsible for patching, updating and monitoring all infrastructure, master and application nodes.
You can employ your own registry, networking, CI/CD tools and storage. Or you may make use of any of the built-in options that can automate application and container builds, source code management, health management, scaling and more.
Here are some key features:
- Access, security and monitoring—allows you to integrate with Azure AD and employ Kubernetes RBAC. It also allows you to keep track of the health of resources and clusters.
- Cluster and node—all nodes of this service run on Azure VMs. The service allows you to connect storage to pods and nodes, you may also upgrade cluster components.
- Service Level Agreement—provides a SLA that provides for 99.95% availability.
- Security—Azure simplifies OpenShift security, which can be difficult to configure in an on-premises environment.
OpenShift 4 on Azure Red Hat OpenShift
With version 4, OpenShift added core attributes to Azure Red Hat OpenShift, such as:
- Support for a cluster-admin role—allows for the cluster-admin role via Azure Red Hat OpenShift clusters, providing entire cluster customization abilities, including installing CRDs and running privileged containers.
- Autoscaling—utilizes the MachineAutoscalers and Cluster Autoscaler to perform Kubernetes autoscaling, expanding or reducing cluster size to fulfill current demand. Pick and choose VM sizes to your workloads.
- Clusters across multiple Availability Zones—to provide high-levels of resilience, cluster components are deployed over three Azure AZs in certain Azure regions to ensure high-availability for your mission-critical and highly-demanding data and applications. Azure Red Hat OpenShift features a SLA of 99.9%.
- Industry standard compliance certifications—to let you adhere to your compliance requirements via regulated markets and industries around the world, Azure Red Hat OpenShift is FedRAMP High, PCI DSS and HITRUST certified. Azure has the largest compliance portfolio in relation to the entire number of offerings, and the amount of customer-facing services.
- Option to use your own identity provider—as well as supporting authorization and authentication via Azure Active Directory, users can make use of their supported identity provider, for instance they can use OpenID Connect or OAuth2.
- Support for Azure Monitor—Microsoft Azure now offers monitoring support for Red Hat OpenShift 4 clusters. Those hosted via Azure Red Hat OpenShift and via OpenShift Container Platform run on Azure or run on-premise via Azure Monitor for containers. At the moment, this support is available in a public preview.
- Support for private ingress and API endpoints—users can now select either public or private cluster management (API) or ingress endpoints. With Azure Express Route and private endpoints, private hybrid clusters have been enabled. This lets mutual users extend their on-premise strategies to Azure.
Image Source: OpenShift
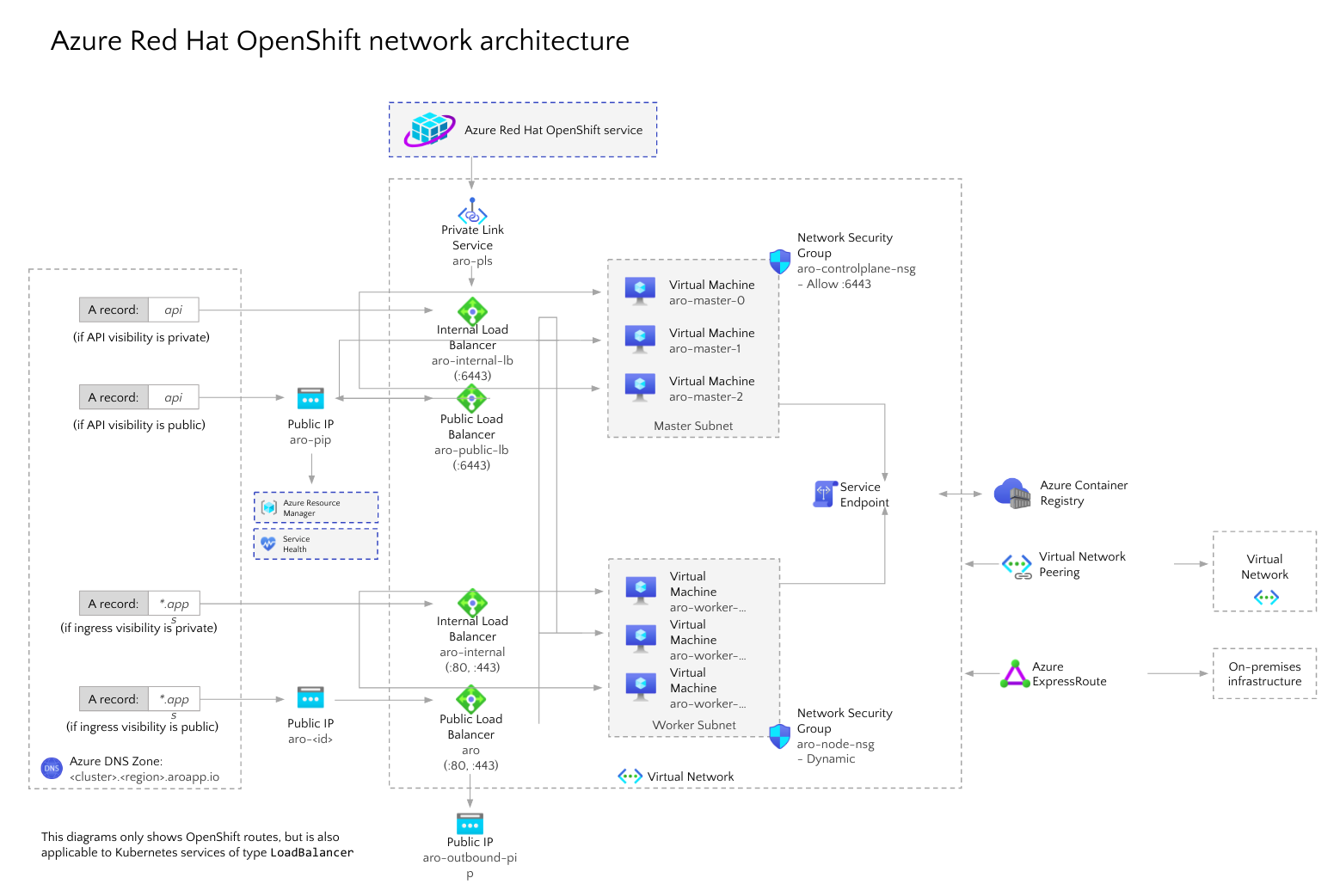
Network Concepts for Azure Red Hat OpenShift
OpenShift Software Defined Networking is an overlay network configured utilizing Open vSwitch, which is an OpenFlow implementation designed according to specifications recommended by the CNI project.
The SDN supports various plugins. Specifically, Azure Red Hat on OpenShift 4 uses the Network Policy plugin. The SDN manages all network communication. This means there is no need to establish any extra routes on your virtual networks in order to achieve pod-to-pod communication.
Image Source: Azure
Once you use Azure Red Hat on OpenShift 4—the entire cluster (including all nodes) is contained inside the virtual network. Master nodes and worker nodes are each placed in their own unique subnet, which is located inside the main virtual network. Each subnet gets its own internal load balancer as well as a public load balancer.
Here are several networking features of Azure Red Hat OpenShift:
- The service lets users create an ARO cluster within an existing virtual network. Alternatively, users can create a virtual network when they create an ARO cluster.
- You can configure Service and Pod Network CIDRs.
- Masters and nodes are located in diverse subnets.
- Masters virtual network subnets and nodes must be minimum /27.
- Pod CIDR default is 10.128.0.0/14.
- Service CIDR default is 172.30.0.0/16.
- Pod and Service Network CIDRs should not overlap with any different address ranges used on the network, and should not be in the cluster’s virtual network IP address range.
- Pod CIDR must be at least /18 in size. The network of the pod is utilized solely within the OpenShift SDN and is non-routable IPs.
- Each node is given /23 subnets (512 IPs) for the pods. You cannot change this value.
- You can’t attach a pod to several networks.
- You can’t configure Egress static IP.
Conclusion
In this article I explained the basics of Azure Red Hat OpenShift, a solution that lets you run OpenShift as a managed service in the Azure cloud. I discussed the benefits of OpenShift 4, recently supported on Azure, which adds features like autoscaling and running clusters across multiple Availability Zones. Finally, I discussed how networking works in the solution, leveraging Azure cloud network infrastructure and Open vSwitch (OVS).
I hope this will be of help as you evaluate moving your OpenShift deployment to the cloud.
By Gilad Maayan

Gilad David Maayan is a technology writer who has worked with over 150 technology companies including SAP, Samsung NEXT, NetApp and Imperva, producing technical and thought leadership content that elucidates technical solutions for developers and IT leadership.