No organization in healthcare, retail, logistics, or any other industry is immune to cyberattacks, outside threats, or internal human errors.
But in healthcare, such risks bring additional consequences, for example, patients’ sensitive data disclosure. Healthcare establishments realize that and start taking actions.
One of the first steps is implementing a cybersecurity framework. It helps organizations define which actions they need to take to handle cybersecurity risks while keeping their patients’ data secure.
What’s a cybersecurity framework, how to implement it, and why—let’s find out in this guide.
What is Healthcare CFS?
Let’s start with the basics.
In simple words, a healthcare cybersecurity framework (or CSF) is a guide that describes how to manage and reduce security risks in hospitals, clinics, and other organizations that deal with sensitive data. It could be e-health records, lab results, or prescriptions.
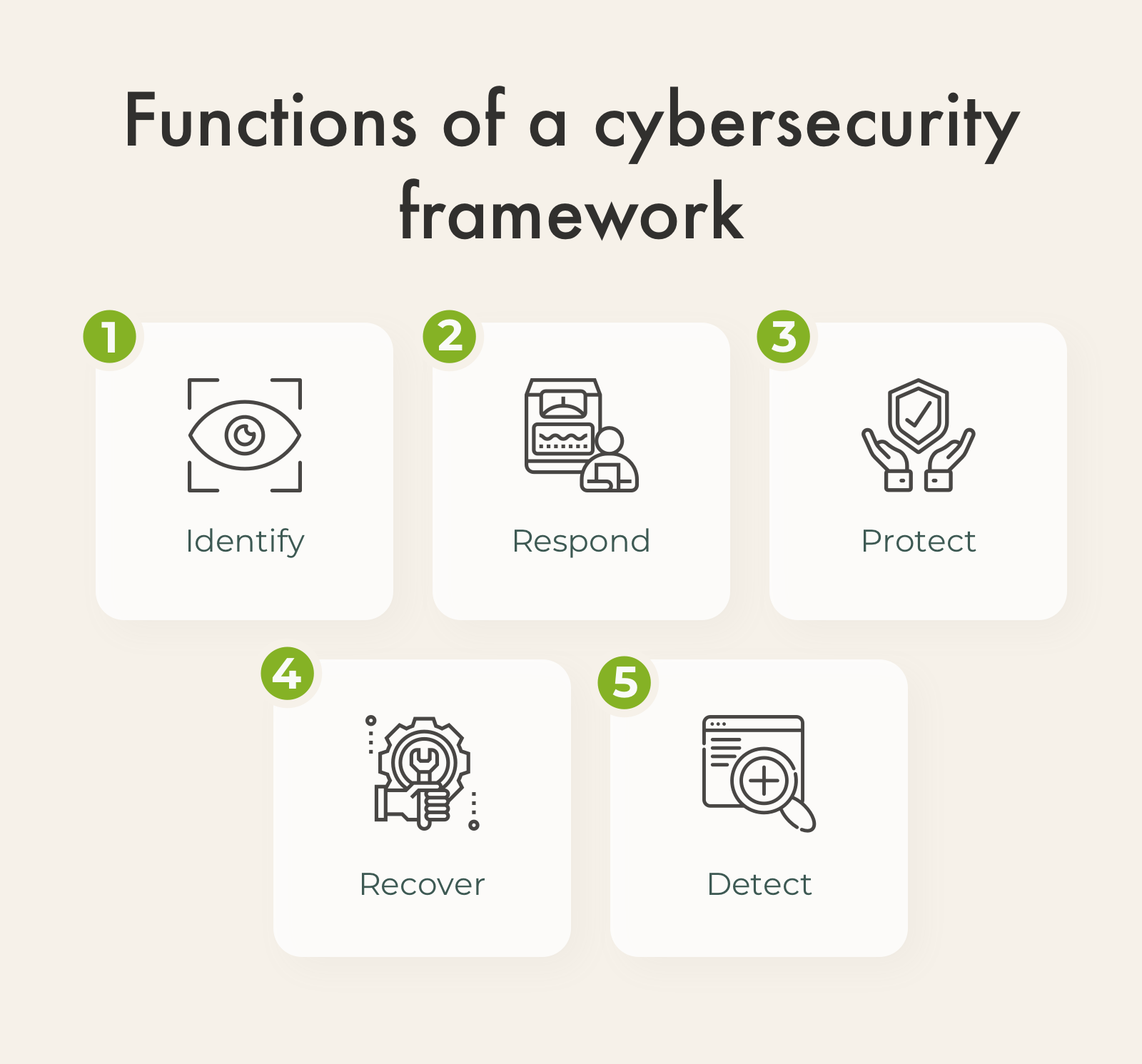
How does a CSF work?
- Identifies and detects security threats, helps to recover from their consequences.
- Ensures that the organization’s security goals align with its business requirements, budget, and risk tolerance.
- Helps to align the company’s business and tech policies.
Healthcare frameworks offer an action plan that explains how to create a new cybersecurity program or improve existing ones. This is done to better understand current cybersecurity risks in an organization and find a way to deal with them.
But it doesn’t mean that a CSF is a set of strict rules. It’s still a guideline with IT security practices that improve existing policies, not a list of instructions.
Besides, even the most common frameworks like NIST or HITRUST shouldn’t be adopted blindly. Instead, cybersecurity frameworks need updates and should be adapted to your current organization and business needs.
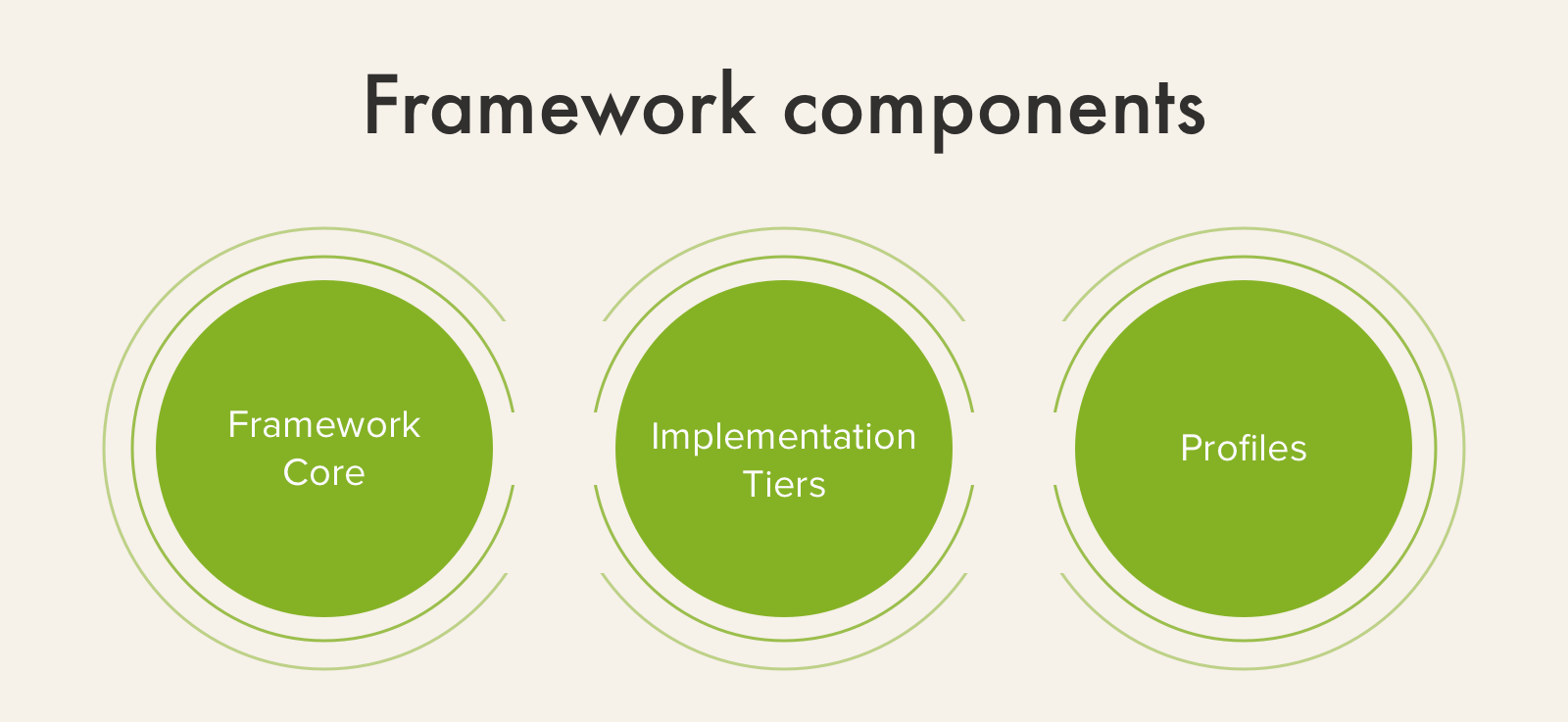
A cybersecurity framework includes three components:
- the core which guides cybersecurity activities and outcomes
- implementation tiers, evaluate the current cybersecurity posture of an organization
- framework profile, a blueprint for minimizing the cyber risks aligned with the organization’s goals
Here are the most prevalent cybersecurity frameworks in healthcare:
The popularity of cybersecurity frameworks according to HIMSS Cybersecurity Survey conducted in 2018.
Do We Need Cybersecurity Frameworks?
If you want to remain compliant with the legislation, protect your organization’s privacy and security, and opt for secure medical software development, it’s undoubtedly a ‘yes’.
Cybersecurity frameworks are must-haves for protecting the organization from malware and ransomware attacks. As well as from malicious insiders, errors, and privilege misuse.
By the way, privilege misuse is a real problem in healthcare. It’s the only industry where insider threats are more dangerous than outside ones. According to the Verison report, more frequent, too: 59% of internal vs. 42% of external incidents.
There are a couple of reasons for that, but human error is the most frequent. Doctors and employees abuse their access to internal systems to check the information they store.
For example, when someone checks on what procedures celebrities take—’just for fun’, in 6% of breach cases.
How to Implement a Cybersecurity Framework?
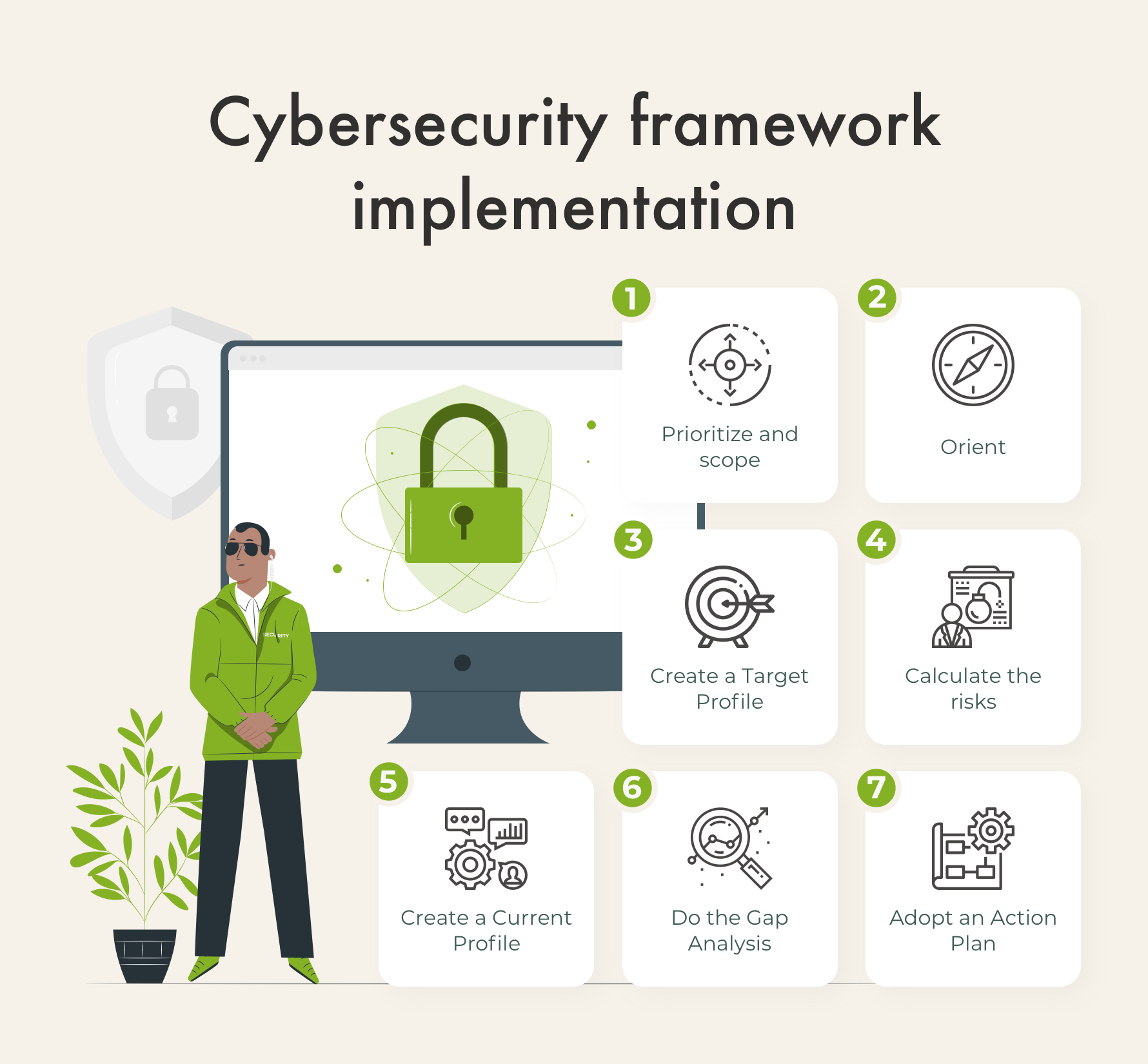
Healthcare organizations need to go through these once they decide to adopt a security framework:
- Step 1: Set your priorities and goals.
- Step 2: Identify current risk management approaches.
- Step 3: Create a risk management profile (or target profile).
- Step 4: Evaluate the risks.
- Step 5: Create a risk management profile under assessment results.
- Step 6: Create an action plan.
- Step 7: Implement the plan.
Let’s consider each of them in detail.
Set your goals
Before implementing a framework, the first thing to do is to set security goals and priorities. Find out what level of risk is acceptable in your organization and which areas need the best protection.
By setting goals, you can organize your actions, establish a scope of security reforms, and prioritize the critical steps.
Identify your current position
First, you need to assess the security tools and practices your company already has. It will show you what’s already working and what needs improvement.
Some healthcare companies partner with third-party software vendors to assess their security levels. Or train their employees to use software tools that score security efforts.
Estimate the risks
Evaluate the level of risk for the current system your organization uses. How can security breaches happen? What will they trigger?
Pay attention to current risks and emerging threats and vulnerabilities to thoroughly understand the outcomes of security events.
Create a risk management profile
Cybersecurity frameworks aren’t set in stone, and you should not blindly follow them. Instead, the best approach is to tailor whatever framework you choose to the company’s needs.
Hospitals, labs, and other healthcare entities make a thorough risk assessment and define their current state.
If the staff has detected security risks, they should document them.
Make an action plan
Start comparing your actual scores with those you want to achieve as you’ve organized the risks and their consequences. And define what you need to do to fill this gap between the current and target score.
Implement the action plan
At this stage, the organization should have:
- a clear picture of security issues they may face
- their defensive means
- target goals
- gaps
- list of actions to take
Once you consider all the details, you can start implementing the framework you’ve picked.
But it’s not enough to adopt an action plan. Healthcare organizations also need to organize and monitor metrics to make sure the framework works as expected.
It’s rather an ongoing process to bring the max profit and further framework customization. In the end, the selected healthcare cybersecurity framework should 100% meet the company’s needs.
How to Enhance Cybersecurity in Healthcare?
Apart from applying security frameworks, you should also consider preventive measures to protect your business from cyber risks. Here are several tips to strengthen the security:
-
- Staff education. It’s critical to consider the training part to ensure healthcare providers are aware of possible risks and be careful when managing sensitive data.
- Strict data access controls. Access restrictions enable patient data protection from unauthorized users. Make sure that only authorized employees of healthcare institutions are allowed to work with clients’ information.
- Data encryption. Encrypting information during transferring and storage enables medical establishments to make it hard for third parties to steal private data.
- Data usage controls. This tip will assist you in controlling and tracking malicious activity. For instance, you can deploy a system to prevent unauthorized actions with user data (uploading to the Internet, copying to external drives, etc.).
- Reducing the Risks of Connected Devices
With the growing popularity of the IoT, connected devices are no longer restricted to mobile phones. Today they can be presented in the form of different medical devices such as blood pressure monitors, ingestible sensors, glucose monitors, etc. Thus, you have to consider the following aspects:
- All connected devices must be deployed on their separate network.
- All devices should be tracked constantly for sudden changes in activity level that could point out a safety issue.
- Remove unnecessary services on devices
- Apply two-factor authentication
- Regularly validate the devices and install upgrades to keep them up to date
Summing Up
Adopting a cybersecurity framework can be challenging due to its constantly changing rules and requirements. However, it’s critical to use these frameworks in the medical sphere to block cybersecurity-related threats on time.
By Yuliya Melnik

Yuliya Melnik is a technical writer at Cleveroad. It is a web and mobile app development company in Ukraine. She is passionate about innovative technologies that make the world a better place and loves creating content that evokes vivid emotions.